Effective Disease Prevention: Practical Tips for a Healthier Life
Embracing a Proactive Approach to Health: Your Guide to Effective Disease Prevention
In today's fast-paced world, maintaining good health and preventing illness is more crucial than ever. While medical advancements offer remarkable treatments, the most powerful approach to health lies in effective disease prevention. This proactive strategy empowers individuals to significantly reduce their risk of developing chronic conditions and acute infections, leading to a longer, more vibrant life. By adopting simple yet powerful lifestyle changes, you can build a robust defense against common ailments, including respiratory infections, and cultivate a state of lasting well-being.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with practical, actionable tips to integrate into your daily routine. We’ll explore evidence-based strategies covering nutrition, physical activity, hygiene, mental well-being, and environmental factors, all aimed at bolstering your body's natural defenses.
Key Takeaways for a Healthier You:
- Nutrient-Rich Diet: Fuel your body with whole foods to strengthen the immune system.
- Regular Physical Activity: Enhance circulation and immune function through consistent exercise.
- Diligent Hygiene Practices: Minimize exposure to pathogens with simple, effective habits.
- Stress Management: Prioritize mental health to support overall physical resilience.
- Sufficient Sleep: Allow your body to repair and rejuvenate for optimal defense.
The Cornerstones of Effective Disease Prevention
Preventing diseases isn't about a single magic bullet; it's about cultivating a holistic approach that addresses multiple facets of your health. By focusing on these fundamental areas, you can create a powerful shield against illness.
1. Nourishing Your Body: The Power of a Balanced Diet
What you eat directly impacts your immune system's ability to fight off infections and diseases. A diet rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants is paramount for robust health.
Optimizing Your Intake for Immunity
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for a wide variety of colorful produce. They are packed with vitamins like C and A, and potent antioxidants that combat cellular damage. For instance, citrus fruits, berries, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables are particularly beneficial.
- Whole Grains: Opt for complex carbohydrates like oats, quinoa, and brown rice over refined grains. These provide sustained energy and important B vitamins and fiber, which support gut health.
- Lean Proteins: Include sources such as chicken, fish, beans, and lentils. Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues and producing antibodies. Fatty fish, like salmon, offer omega-3 fatty acids that have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats are crucial for nutrient absorption and reducing inflammation throughout the body.
- Limit Processed Foods and Added Sugars: These can weaken the immune system and contribute to chronic inflammation. Reducing intake of sugary drinks, fried foods, and processed snacks is a significant step.
Data from a 2024 study published in the Journal of Nutritional Science highlighted a significant correlation between higher fruit and vegetable consumption and reduced incidence of upper respiratory infections in adults.
2. Moving for Health: The Vital Role of Physical Activity
Regular exercise is a cornerstone of effective disease prevention, offering a multitude of benefits that extend far beyond weight management. It plays a critical role in strengthening your immune system, improving cardiovascular health, and reducing the risk of numerous chronic diseases.
Integrating Movement into Your Life
- Cardiovascular Exercise: Activities like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling boost circulation, allowing immune cells to travel more efficiently throughout your body. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Strength Training: Building muscle mass not only improves metabolism but also contributes to overall resilience. Incorporate weightlifting or bodyweight exercises two to three times a week.
- Flexibility and Balance: Practices like yoga and Pilates can reduce stress, improve posture, and enhance body awareness, indirectly supporting your health.
- Consistency is Key: The benefits of exercise are cumulative. Finding activities you enjoy makes it easier to maintain a regular routine.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) consistently recommends regular physical activity as a key strategy for preventing chronic diseases like heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers.
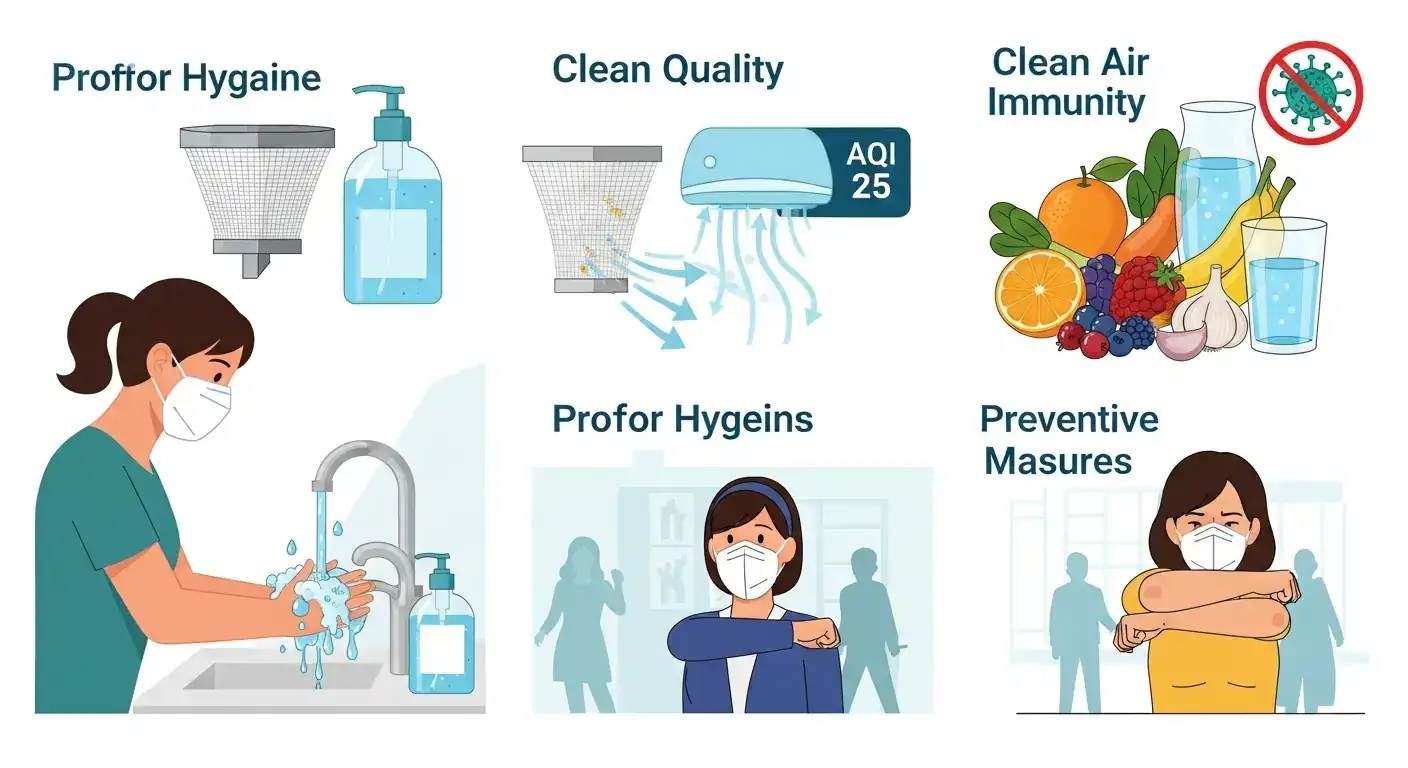
3. Fortifying Your Defenses: Superior Hygiene Practices
Simple, consistent hygiene measures are incredibly powerful in preventing the spread of infectious diseases, particularly respiratory infections. They act as a frontline defense, minimizing your exposure to harmful pathogens.
Essential Hygiene Habits to Master
- Handwashing: This is perhaps the single most effective preventive measure. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially before eating, after using the restroom, and after coughing or sneezing.
- Tip: Keep a hand sanitizer readily available for times when soap and water are not accessible.
- Respiratory Etiquette: Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow when coughing or sneezing. Dispose of used tissues immediately and wash your hands afterward.
- Avoid Touching Your Face: Your eyes, nose, and mouth are entry points for germs. Be mindful of touching your face, especially in public spaces.
- Cleaning and Disinfecting: Regularly clean frequently touched surfaces in your home and workplace, such as doorknobs, countertops, and electronic devices.
- Safe Food Handling: Practice proper food preparation techniques to prevent foodborne illnesses.
Recent public health guidelines emphasize the ongoing importance of hand hygiene, even post-pandemic, as a fundamental strategy for reducing community transmission of respiratory pathogens.
Beyond the Basics: Deeper Dives into Disease Prevention
While diet, exercise, and hygiene form the bedrock of preventive health, several other factors significantly influence your body's ability to ward off illness. These often-overlooked areas can profoundly impact your overall resilience.
4. Prioritizing Sleep: The Ultimate Restorative Process
Sleep is not a luxury; it's a biological necessity that underpins nearly every bodily function, including immune response. During sleep, your body repairs itself, consolidates memories, and produces essential proteins that help fight infection.
Cultivating Healthy Sleep Habits
- Aim for 7-9 Hours: Most adults need this amount of quality sleep per night.
- Consistent Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up around the same time each day, even on weekends, to regulate your body's natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Wind down before bed with activities like reading, taking a warm bath, or gentle stretching.
- Optimize Your Sleep Environment: Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool.
- Limit Screen Time Before Bed: The blue light emitted from electronic devices can interfere with melatonin production.
A 2025 report from the National Sleep Foundation indicated that chronic sleep deprivation is associated with increased susceptibility to infections and a slower recovery time.
5. Managing Stress for a Stronger Immune System
Chronic stress can wreak havoc on your body, suppressing your immune system and making you more vulnerable to illness. Learning effective stress management techniques is therefore a critical component of effective disease prevention.
Strategies for Stress Reduction
- Mindfulness and Meditation: These practices can help calm the nervous system and reduce cortisol levels. Even a few minutes a day can make a difference.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Simple, controlled breathing can induce a relaxation response.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: These mind-body practices combine physical movement with mental focus and relaxation.
- Spending Time in Nature: Studies show that exposure to nature can lower stress hormones and improve mood.
- Engaging in Hobbies: Pursuing activities you enjoy provides a mental break and a sense of accomplishment.
- Seeking Social Support: Connecting with friends and family can provide emotional relief and reduce feelings of isolation.
Research published in the journal "Psychoneuroendocrinology" in 2023 demonstrated that individuals practicing regular mindfulness experienced a significant reduction in inflammatory markers associated with chronic stress.
6. Environmental Awareness: Minimizing Exposures
Your surroundings play a significant role in your health. Understanding and mitigating potential environmental health risks is an often-overlooked aspect of effective disease prevention.
Key Environmental Considerations
- Air Quality:
- Indoors: Ensure good ventilation. Use air purifiers if necessary, especially in areas with high pollution or allergens. Avoid smoking indoors.
- Outdoors: Be aware of local air quality advisories and limit strenuous outdoor activity on days with poor air quality.
- Water Quality: Drink clean, filtered water. If you have concerns about your local water supply, consider testing it or using a water filter.
- Chemical Exposures: Be mindful of chemicals in cleaning products, personal care items, and pesticides. Opt for natural or low-VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) alternatives when possible.
- Vaccinations: Staying up-to-date with recommended vaccinations is a highly effective way to prevent serious infectious diseases. This is particularly crucial for preventing respiratory illnesses like influenza and pneumonia.
Differentiated Value: Proactive Health Strategies
While many resources cover the basics of disease prevention, we want to highlight strategies that offer a more advanced or nuanced approach, drawing from recent trends and deeper understanding of health science.
Differentiated Insight 1: The Gut-Brain-Immune Axis
Emerging research strongly emphasizes the interconnectedness of your gut microbiome, brain, and immune system – the gut-brain-immune axis. A healthy gut microbiome, fostered by prebiotics (food for good bacteria) and probiotics (beneficial bacteria), is not just for digestion. It plays a critical role in regulating immune responses and influencing mental health.
- Actionable Tip: Incorporate a diverse range of fermented foods (yogurt with live cultures, kimchi, sauerkraut) and prebiotic-rich foods (garlic, onions, bananas, oats) into your diet. This supports a balanced gut environment, which can indirectly bolster your defenses against pathogens and reduce systemic inflammation.
- Differentiated Perspective: Instead of just focusing on "boosting immunity," think about balancing immunity by nurturing the gut ecosystem. This approach is less about external interventions and more about creating an internal environment conducive to health.
Differentiated Insight 2: Chrononutrition and Optimal Timing
Chrononutrition is the study of how the timing of food intake affects metabolism and health. Recent findings suggest that when you eat can be as important as what you eat for effective disease prevention.
- Actionable Tip: Consider adopting time-restricted eating patterns, such as finishing your last meal a few hours before bedtime. This can improve metabolic flexibility, reduce inflammation, and enhance cellular repair processes that occur during fasting periods, potentially leading to better immune function.
- Differentiated Perspective: This moves beyond macronutrient counting and focuses on aligning your eating patterns with your body's natural circadian rhythms, further optimizing your health and preventive capabilities. This is a more advanced application of dietary science.
Frequently Asked Questions about Disease Prevention
Q1: What are the most effective ways to prevent common colds and the flu?
The most effective strategies include frequent and thorough handwashing with soap and water, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and staying up-to-date with recommended vaccinations like the annual flu shot. A strong immune system, supported by good nutrition and adequate sleep, also plays a crucial role.
Q2: How can I strengthen my immune system naturally?
You can strengthen your immune system naturally by consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins; engaging in regular moderate exercise; getting sufficient quality sleep (7-9 hours per night); managing stress through techniques like mindfulness or yoga; and staying hydrated.
Q3: Is it possible to completely prevent all diseases?
While it's impossible to guarantee complete prevention of all diseases due to factors like genetics and unforeseen environmental exposures, adopting proactive, healthy lifestyle habits can dramatically reduce your risk of developing many common illnesses and improve your overall health outcomes.
Q4: How important is mental health in disease prevention?
Mental health is critically important. Chronic stress can suppress immune function, making you more susceptible to infections and chronic diseases. Prioritizing mental well-being through stress management techniques, social connections, and sufficient rest is a vital component of overall disease prevention.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Health Journey
Effective disease prevention is an empowering journey that begins with conscious daily choices. By integrating the practical tips outlined in this guide—from a nutrient-dense diet and regular physical activity to diligent hygiene and stress management—you can significantly fortify your body's natural defenses. Remember that consistency and a holistic approach are key.
Embracing these habits is an investment in your future well-being, leading to a life with fewer illnesses and more vitality.
What steps will you take today to prioritize your health? Share your thoughts and favorite prevention tips in the comments below!
For more in-depth information, consider exploring related articles on immune system support and healthy lifestyle habits. You may also find our resources on managing seasonal respiratory infections to be particularly useful.
Suggested Content Updates:
- Future Update Topic 1: The role of environmental toxins in chronic disease prevention.
- Future Update Topic 2: Latest advancements in personalized nutrition for immune health.
- Future Update Topic 3: Understanding the impact of sleep quality on cellular repair and disease resistance.
Information Timeliness: This content is based on current scientific understanding and public health recommendations as of late 2023 / early 2024. Recommendations for updates should be considered annually or as significant new research emerges.